User Guide For Hospital Management System v2.0
Table of content
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Features
- 3. Command Format
- 4. Command Usage
- 5. Command Summary
- 6. FAQ
1. Introduction
This document serves as a user guide for HAMS. It teaches the user how to install HAMS, describes the features of HAMS, explains how HAMS can be used and finally answer some frequently asked questions about HAMS.
HAMS is a CLI-based medical facility administration system that assists in the maintenance of various medical records.
HAMS is designed for administrative assistants in medical facilities, like hospitals or polyclinics, that prefer using CLI to keep track of various medical records and can type fast.
1.1 Starting HAMS
- Ensure you have JDK 11 installed on your computer. You can download the installer for your OS from here.
- Download the latest .jar file release for HAMS from GitHub.
- Move the .jar to an empty folder.
- Open Command Prompt.
- In Command Prompt, change your current working directory to the folder containing the .jar using $
cd <Path of folder containing .jar> - Run the .jar using $
java -jar (latest version).jar
Back to top ↑
2. Features
Keep track of different record types
HAMS provides you with an easy-to-use system that helps manage and keep track of two types of medical records: Patients and Appointments.
View all your tasks
The lista or listp command that HAMS provides can display all the Appointment or Patient records within the system in a readable format.
Auto-save and store these records
HAMS has an auto-save feature which stores Patient and Appointments every time you add or modify them. With this feature, your tasks will be saved every time you leave the application and can be easily retrieved when you reopen the application subsequently.
Back to top ↑
3. Command Format
Words enclosed within angle brackets [] are the parameters to be supplied by the user. Other keywords stated are compulsory and they should be included.
For example, in adda \date [date] \time [time] \pid [patient id], adda is the command keyword that adds an Appointment record.
\date and \time are compulsory labels to denoting what field the subsequent information belongs to.
[date] is the date of the appointment to be supplied by you. [time] represents the time of the appointment to be supplied by you.
A valid input would be adda \date 22/05/2020 \time 1200 \pid 1.
Back to top ↑
4. Command Usage
4.1 Patient Commands
4.1.1 Add a new Patient record
The program allows you to add a new Patient record to the current list of Patient records. Note that patient id number (pid) is decided by HAMS and not the user. Pid assigned may not be in order.
Format: addp \name [name] \age [age] \address [address] \phone [phone]
addpkeyword\namefollowed by the name of the patient\agefollowed by the age of the patient\addressfollowed by the address of the patient\phonefollowed by the contact number of the patient
Examples of Usage
| OK? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| OK | addp \name Justin \address Pasir Ris \age 20 \phone 98889888 |
|
| OK | addp \age 20 \phone 98889888 \name Justin \address Pasir Ris |
|
| NOT OK | addp |
4.1.2 List all existing Patients
The program allows you to list all existing Patients. The command simply contains the ‘listp’ keyword.
Format: listp
Example of usage:
| Is Patient list empty? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| NO | listp |
|
| YES | listp |
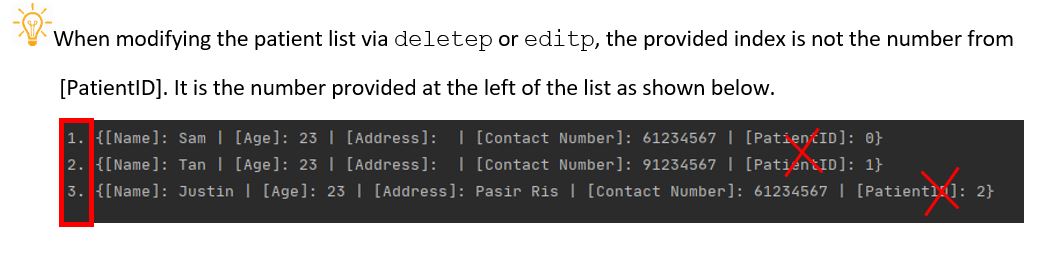
4.1.3 Delete an existing Patient
The program allows you to delete an existing Patient record by its index in the list.
Format: deletep \index [index number in list]
deletepkeyword\indexfollowed by the index number of the patient to be deleted
Example of usage:
| OK? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| OK | deletep \index 2 |
 |
| NOT OK | deletep \index a |
 |
4.1.4 Edit an existing Patient
The program allows you to make changes to an existing Patient record by its index in the list. Note that you cannot edit the patient id number.
Format: editp \index [index number in list] \name [name] \age [age] \address [address] \phone [phone]
editpkeyword\indexfollowed by the index number of the Patient record in the list\namefollowed by the name of the patient\agefollowed by the age of the patient\addressfollowed by the address of the patient\phonethe contact number of the patient
Example List (Before)
Examples of usage:
Please refer to the above “Before” list to compare the changes.
| OK? | Usage | Outcome & After |
|---|---|---|
| OK | editp \index 2 \name Lam \phone 83487846 |
|
| OK | editp \age 99 \address Bedok \phone 89993999 \name Justin \index 3 |
|
| NOT OK | editp \index a \address Paris Ris \phone 93489678 |
Final List
4.1.5 Find an existing patient
The program allows you to find to an existing Patient record based on a search value.
Format: findp [search value]
findpkeywordsearch valuefollowed by a search value.
Example list
Examples of usage:
Please refer to the example list above
| Does it exist in list? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| YES | findp kurumi |
|
| NO | findp ayame |
4.1.6 Clear patient records
The program allows you to clear the patient list.
Format: clearp
Example list
Example of usage:
Please refer to the example list above
| Usage | Outcome & After |
|---|---|
clearp |
Back to top ↑
4.2 Appointment Commands
4.2.1 Add a new Appointment record
The program allows you to add a new Appointment record to the current list of Appointment records. With the addition
of the pid field, it allows users to link the appointment to a specific patient.
The pid provided must be linked to a patient that currently exists in the system.
Format: adda \date [date] \time [time] \pid [patient id]
addakeyword\datefollowed by the date of the appointment\timefollowed by the time of the appointment\pidfollowed by a unique Patient ID (pid).
Example of usage:
| OK? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| OK | adda \date 14/03/2020 \time 1000 \pid 1 |
|
| NOT OK | adda \date 14/03/2020 |
|
| NOT OK | adda \date 31/02/2020 \time 1234 \pid 1 |
4.2.2 List all existing Appointments
The program allows you to list all existing Appointments. The command simply contains the ‘lista’ keyword.
Format: lista
Example of usage:
| Is Appointment list empty? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| NO | lista |
|
| YES | lista |
4.2.3 Delete an existing Appointment
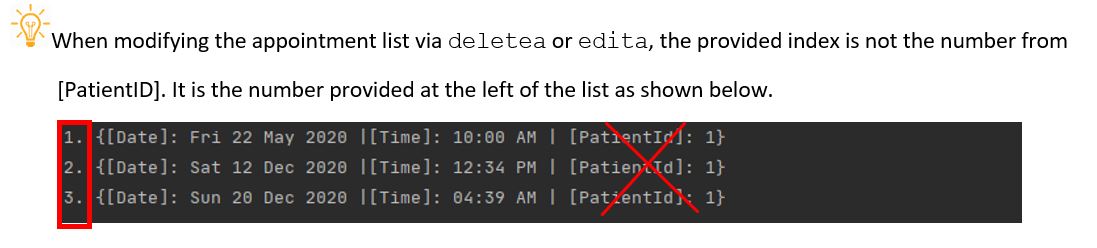
The program allows you to delete an existing Appointment record by its index in the list.
Format: deletea \index [index number in list]
deleteakeyword\indexfollowed by the index number of the Appointment to be deleted
Examples of Usage
| OK? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| OK | deletea \index 3 |
|
| NOT OK | deletea \index 999 |
4.2.4 Edit an existing Appointment
The program allows you to make changes to an existing Appointment record by its index in the list.
Format: edita \index [index number in list] \date [date] \time [time]
editakeyword\indexfollowed by the index number of the Appointment in the list.\datefollowed by the date of the appointment\timefollowed by the time of the appointment
Example List (Before)
Example of usage:
Please refer to the above “Before” list to compare the changes.
| OK? | Usage | Outcome & After |
|---|---|---|
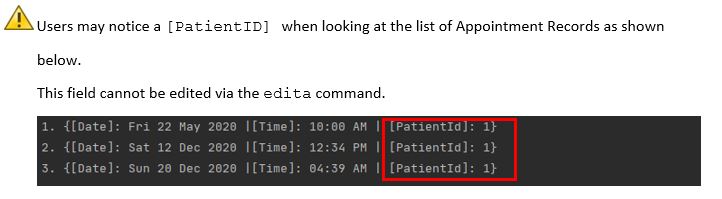
| OK | edita \index 3 \date 20/05/2021 \time 2300 |
|
| OK | edita \index 1 \time 1300 |
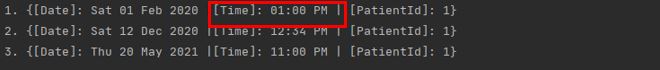 |
| NOT OK | edita |
Final list:
4.2.5 Find an existing Appointment
The program allows you to find to an existing Appointment record based on a search value. The search value must follow the date format of dd/mm/yyyy or time format of hh:mm a.
Format: finda [search value]
findakeywordsearch valuefollowed by a search value.
Example list:
Example of usage:
Please refer to the example list above
| Does it exist in list? | Usage | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| YES | finda 22/05/2020 |
|
| NO | finda 23/05/2020 |
4.2.6 Clear appointment records
The program allows you to clear the appointment list.
Format: cleara
clearakeyword
Example list
Example of usage:
Please refer to the example list above
| Usage | Outcome & After |
|---|---|
cleara |
Back to top ↑
4.3 Clear all records
The program allows you to clear all lists.
Format: clearall
clearallkeyword
Example list
Example of usage:
Please refer to the example lists above
| Is both list empty? | Usage | Outcome & After |
|---|---|---|
| NO | clearall |
Back to top ↑
4.4 View help
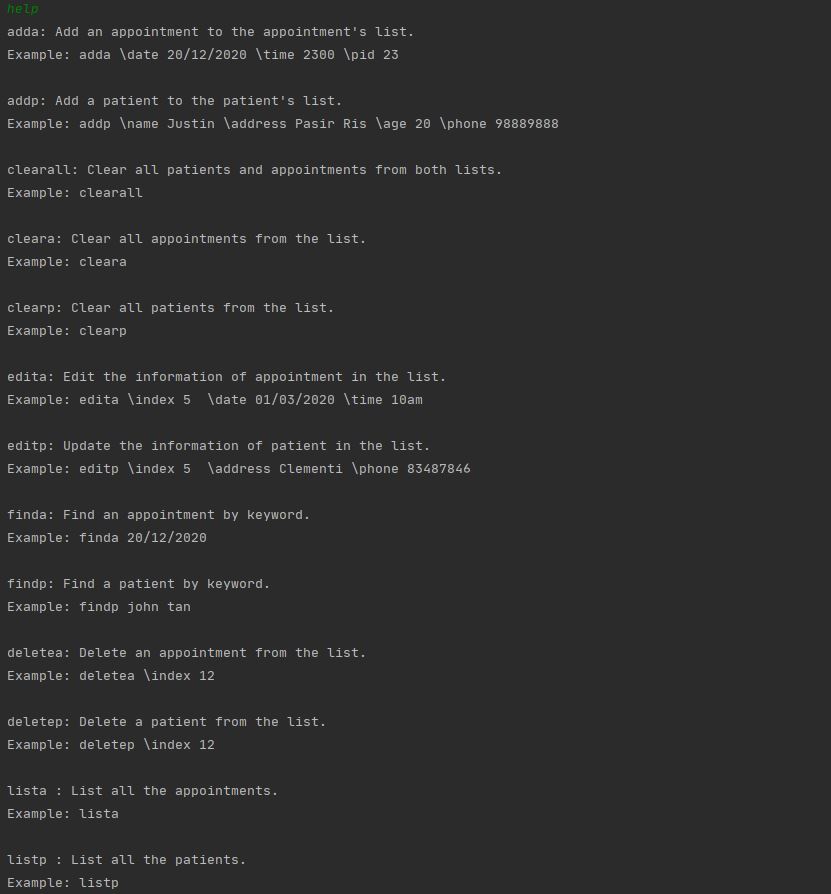
The ‘help’ keyword provides you with a list of valid commands, their functions and their proper usages.
Format: help
Example of usage:
help
Expected outcome
Back to top ↑
4.5 Exit HAMS program
This command exits the HAMS program and saves the current Patient/Appointment data into separate local save files (in
/saves/appointments.txt and /saves/patients.txt respectively). Also, the resuable and new patient ids will be saved in
/saves/patientId.txt. These files will be loaded to the program when it is run again subsequently.
Format: exit
Example of usage:
exit
Expected outcome:
Back to top ↑
5. Command Summary
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
adda \date [date] \time [time] \pid [pid] |
Adds date and time of an appointment and links it to a patient based on their id |
addp \name [name] \age [age] \address [address] \phone [phone] |
Adds name, age, address, and contact number of patient |
finda [search value] |
Searches through all appointment records for the search value |
findp [search value] |
Searches through all patient records for the search value |
lista |
List all the appointments from the appointment’s list |
listp |
List all the patients from the patient’s list |
cleara |
Clears all appointment records |
clearp |
Clears all patient records |
clearall |
Clears both appointment and patient records |
deletea \index [index number in list] |
Delete an appointment by the list’s appointment number |
deletep \index [index number in list] |
Delete a patient by the list’s patient number |
edita \index [index number in list] \date [date] \time [time] |
Edit date or time of an appointment by the list’s appointment number |
editp \index [index number in list] \name [name] \age [age] \address [address] \phone [phone] |
Edit date or time of an appointment by the list’s appointment number |
help |
Give you a manual on a list of valid commands and their usage |
exit |
Exit the program and save the task into an offline data file (in /saves/appointments.txt or /saves/patients.txt) |
Back to top ↑
6. FAQ
Q: Would my details be captured if I randomize the input order of the keywords?
addp \phone 12345678 \address NUS \age 22 \name John Doeaddp \name John Doe \address NUS \ age 22 \ phone 12345678
A: Yes. The system is keyword-sensitive. Regardless of the order given, it stores the information within each command used respectively. Both examples provided above would result in the same information stored.
Q: Why does my patient list does not display any value in the age field?
{[Name]: Tommy | [Age]: | [Address]: | [Contact Number]: 92331234}
A: The age supplied might not be in the correct format (eg age given is a negative number or as a string).
Q: Why am I not able to find anything using finda or findp?
A: Please note that all search values are case-sensitive. For example, Sam will not match with sam
because of the first letter capitalization.
Q: What is pid for in the command adda?
A: pid stands for Patient ID, it is a unique ID tag to each patient. In order to link appointments
to the patient, the pid tag must be present.
Q: I accidentally put in the wrong Patient ID when adding an appointment using adda. How can I change the patientID?
A: Unfortunately upon entering the Patient ID in adda, there is no way of changing the Patient ID. Please remove the incorrect appointment and add the correct appointment in again.
Q: Why when I try to delete a patient in the list, some appointments are being deleted also?
A: Because once you delete a patient, all the appointments related to him/her (through an attribute called pid) are deleted also. Only when there are no appointments
related to the patients, they are not deleted.
Q: Why when I try to clear all the patients in the patient list, the appointments are cleared also?
A: The reason is that there is a dependency of appointments on patients. Each patient can be assigned to multiple appointments through pid. Like mentioned in the previous
question, you can realize that once we clear all the patients, the presence of such appointments are no longer valid (All appointments belong to all patients). Hence, they are cleared
also.